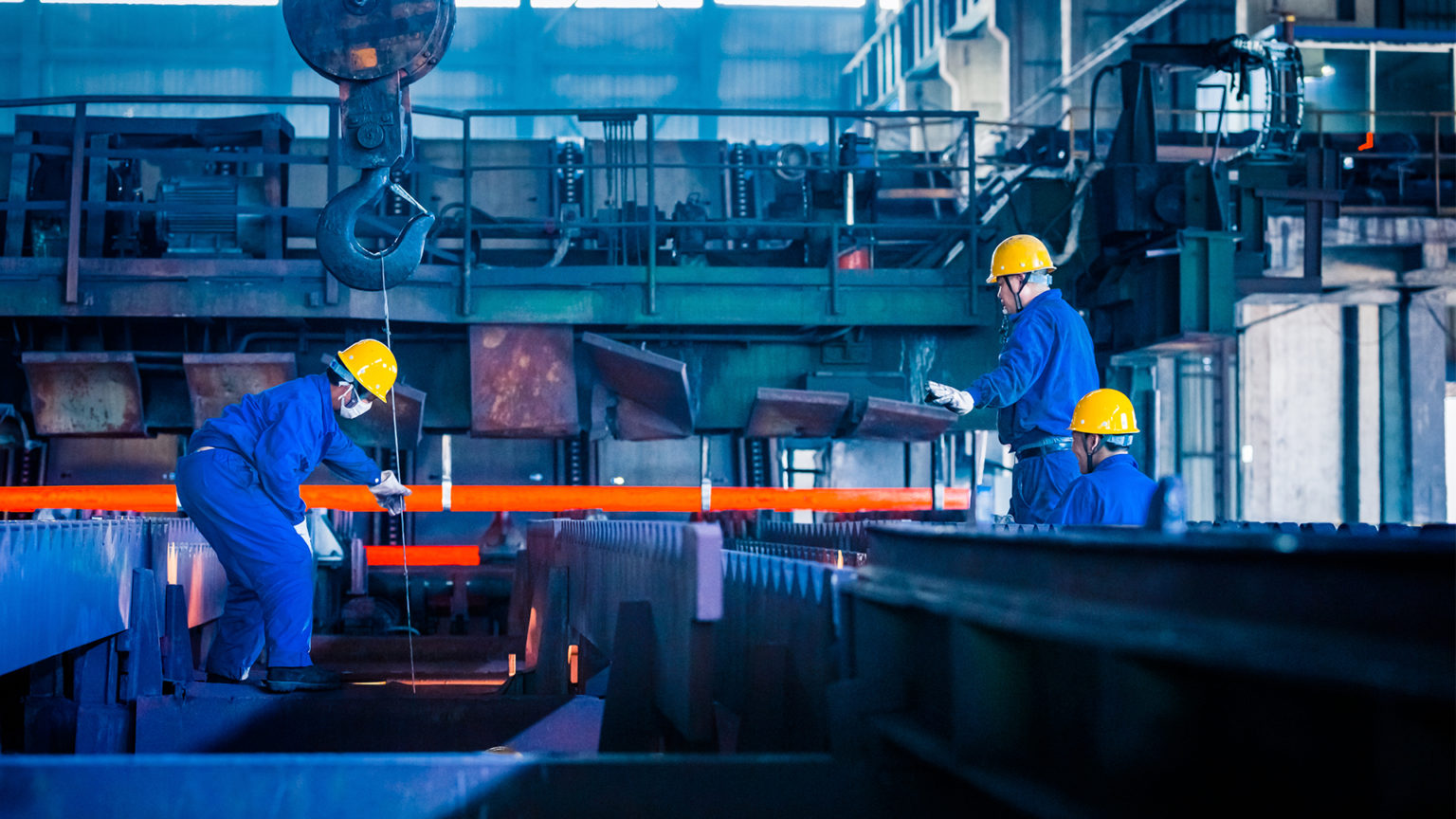
ISO 11611 and ISO 116112 - Liquid Metal
Clothing against liquid metal must guarantee maximum protection to the user for the performance of their activities. It is necessary to analyze the requirements of ISO 11611 and / or ISO 11612 protection standards, which will provide essential information for choosing the correct product.
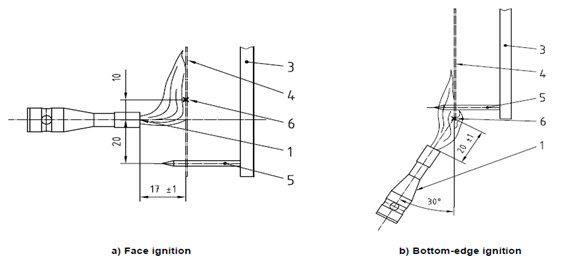
Regarding the projection of molten metal, the fabric must be approved according to ISO 11612. In the first test method of this standard, classified as A1, the flame is in perpendicular contact with the fabric face.
In the second method, classified as A2, the flame is in contact with the lower edge of the fabric at an angle of 30°. To pass this test, in both procedures, the fabric must meet the following requirements:
• The flame must not reach the top or the sides of the sample;
• No sample can be punctured;
• No sample can melt, burn, or present burning residue;
• The average after-flame time must be ≤ 2 s;
• The average after-luminescence time must be ≤ 2 s;
This is the basic requirement for proving the FR characteristics of a given fabric. Only after approval in this test, the fabric can be submitted to the other tests of the standard, namely:
• Method B: It must reach at least level B1.
• Method C: radiant heat. It must reach at least level C1.
• Method D: projection of molten aluminum. It must reach at least level D1.
• Method E: projection of molten iron. It must reach at least level E1
• Method F: heat by contact. It must reach at least level F1.
Fabrics designed to protect against molten metal projection must meet the requirements of the test methods classified as D and / or E, that is, protect against aluminum and iron, respectively. Both tests are performed by projecting a limited amount of metal onto the fabric. It is subsequently evaluated whether there was damage (carbonization, puncture or ignition) in the material.
As for protection against weld spatter, the fabric must be approved according to the ISO 11611 standard, which will measure the amount of spatter necessary for the fabric to have its temperature raised by 40 ° C. In this standard there are two classifications:
• Class 1: More than 15 weld spatters.
• Class 2: More than 25 weld spatters.

